
#Chromatic scale piano plus#
The harmonic chromatic scale is the same whether rising or falling and includes all the notes in the major, harmonic minor or melodic minor scales plus flattened second and sharpened fourth degrees. Two types of chromatic scale have been suggested, the harmonic and the melodic. It has been left to music theorists to offer various suggestions but, in general, composers have ignored them. Composers have been strikingly inconsistent in this area. There is no universal notation that remains unvaried as one moves from key to key. With the chromatic scale there is no widely used notational 'convention' and problems occur when chromatic scale progressions occur within pieces of music in different keys. When chromatic notes are introduced, the sense of key is generally weakened. What is important is that diatonic passages tend to have a sense of key about them. The terms diatonic and chromatic can be extended to any groups of notes, musical phrases, scale passages, chords and harmonies as we shall find later. We will meet other symmetrical scales in lesson 25.

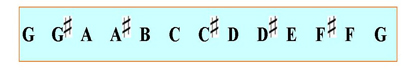
Some notes of a chromatic scale are chromatic to the key note (in this case the first note) while others are diatonic. We have already met the chromatic scale, one example of a symmetrical scale, those constructed from a repeating pattern of intervals (in this case, a semitone or half-step).

We have more to say on this in the next lesson.ĭo not confuse chromatic notes with chromatic scales. However, in the key of E, both C and D sharp are diatonic because both appear in the scale of E harmonic minor.

In the key of C, D sharp will be a chromatic note. When examining the relationship between notes, the key is a vital element. In this key, any other note will be chromatic. In the key of C the notes C, D, E flat, E, F, G, A flat, A, B flat and B are diatonic because they appear in one or more of the major, natural minor, melodic minor or harmonic minor scales. Notes that are not part of these scales are said to be chromatic - those notes are chromatic notes. Intervals between notes that form the scale of a particular key are said to be diatonic. The Diatonic Scale :: The Chromatic Scale :: Harmonic Chromatic Scale :: Melodic Chromatic Scale Thomas Jefferson (1743-1826) 3rd United States president Previous lesson :: next lesson :: contents :: index :: manuscript paper :: comments or queries? To use the menu you must first enable javascript


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
